r package for dropping terms for likelihood ratio test|likelihood ratio test example : store Likelihood Ratio Test. Description. Likelihood ratio test with given fitting results, sample size, number of parameters, log-likelihoods, and alpha. Usage. LRT(n, pFull, pReduced, .
Confira classificações, forma dos times em casa e fora, estatísticas de over e under e tabelas de artilharia de Liga de Acesso 2022/2023 em Soccer24.com.
{plog:ftitle_list}
Resultado da 26 de jan. de 2023 · Senegal and Mauritania set out to book their place in the last four of the 2023 African Nations Championship in Friday's encounter at Stade 19 Mai 1956.. Awaiting the winner of this tie in the .
r likelihood test
We will use the lrtest () function from the lmtest package to perform a likelihood ratio test on these two models: library(lmtest) . #fit full model . model_full <- lm(mpg ~ disp + .1 Answer. Wald Z-tests. For balanced, nested LMMs where df can be computed: Wald t-tests. Likelihood ratio test, either by setting up the model so that the parameter can be . model_1_mom_1_regression <- lm(model_1_mom_1$ff4f_actual_excess_return_month1 ~ .
Likelihood Ratio Tests. Likelihood ratio tests are used to compare the goodness of fit of two statistical models. The LRT compares two hierarchically nested models to determine whether .
Compute the test of a one-dimensional (vector) contrast in a linear mixed model fitted with lmer from package lmerTest. The contrast should specify a linear function of the mean-value .
Likelihood Ratio Test. Description. Likelihood ratio test with given fitting results, sample size, number of parameters, log-likelihoods, and alpha. Usage. LRT(n, pFull, pReduced, . We will use the lrtest () function from the lmtest package to perform a likelihood ratio test on these two models: library(lmtest) #fit full model. model_full #fit reduced model. . The Likelihood Ratio Test is a staple in the toolkit of many statisticians and researchers. With its ability to compare nested models, it offers insights into the necessity (or .
The formula for the likelihood ratio test is given below: Λ= -2log (L (restricted model)/L (full model)) where, L (restricted model): is the likelihood of the restricted model (null .
The likelihood ratio test is defined as -2*log(likelihood model 1/likelihood model 2).The resulting test statistic is assumed to follow a chi-squared distribution, with degrees of freedom (df) equal to the difference of the df between the models. If the test is statistically significant, the model with more variables fits the data significantly .Try fitting all models that differ from the current model by dropping a single term, maintaining marginality. This function is generic; there exist methods for classes lm and glm and the default method will work for many other classes.
The LR.Sarlm() function provides a likelihood ratio test for objects for which a logLik() function exists for their class, or for objects of class logLik. LR1.Sarlm() and Wald1.Sarlm() are used internally in summary.Sarlm() , but may be accessed directly; they report the values respectively of LR and Wald tests for the absence of spatial .Note. Both fit1 and fit2 must have the same family and link function.. Author(s) Damiao N. da Silva [email protected]. Antonio Hermes M. da Silva-Junior [email protected]. References. McCullagh P, Nelder J (1989). Generalized Linear Models.Chapman & Hall/CRC, London. $\begingroup$ The text warning about boundary effects is in a section about choosing the best RE structure in your model by comparing models that differ in their RE structure (ie. same FE). When mentioning using the Likelyhood ratio test to test between two models with different RE structures, Zuur warns about boundary effects and that p-values have to be adjusted.The \chi^2 test can be an exact test (lm models with known scale) or a likelihood-ratio test or a test of the reduction in scaled deviance depending on the method. For glm fits, you can also choose "LRT" and "Rao" for likelihood ratio tests and Rao's efficient score test.
The default test is AIC. The direction parameter can be "both", "backward", or "forward". The following example does an F-test of the terms of the OLS model from above and a likelihood ratio test for several possible terms to the GLM model from above. Using drop1() and add1(). drop1 (mod, test = "F")lrtest is a generic function for carrying out likelihood ratio tests. The default method can be employed for comparing nested (generalized) linear models (see details below). Rdocumentation . gnp + gnp1, data = usdl) fm2 <- lm(con ~ gnp + con1 + gnp1, data = usdl) ## various equivalent specifications of the LR test lrtest(fm2, .

probability ratio test in r
numeric; the density of the grid at which to compute the standardized likelihood function. A beta grid is defined as the grid of values for the SNP parameter used to evaluate the likelihood function. bse: numeric; the number of beta standard errors to utilize in constraining the beta grid limits. Beta grid is evaluated at \beta +/- bse*s.e. lolim To be able to appraise whether including a quadratic effect of dist_settlements improves the model fit, you should fit a model without the squared term (i.e. only the linear effect of dist_settlements) and a model with the squared term. Then perform a likelihood ratio test to appraise whether inclusion of complex terms improves the model fit.The test statistic for the LRT follows a chi-squared distribution with degrees of freedom equal to the difference in dimensionality of your models. The equation for the test statistic is provided below: . Using R for Likelihood Ratio Tests. Before you begin: Download the package “lmtest” and call on that library in order to access the . Likelihood ratio test checks the difference between -2*logLikelihood of the two models against the change in degrees of freedom using a chi-squared test. It is best applied to a model from 'glm' to test the effect of a factor with more than two levels. The records used in the dataset for both models MUST be the same.
That's a Wald test, not a likelihood-ratio test. A few hints for getting beyond this problem. First, once the rms package is loaded the rcs() function should be accessible to the standard coxph() function. See if that works. Second, the rms package inherits its own imputation function, aregImpute(), from the Hmisc package.
character string saying “Likelihood-ratio Test”. data.name character vector of length two giving the names of the datasets used for the test (if “fevd” objects are passed) or the negative log-likelihood values if numbers are passed, or the names of x and y.a formula giving the terms to be considered for adding or dropping. scale: Currently ignored (included for S3 method compatibility) test: should the results include a test statistic relative to the original model? The \chi^2 test is a likelihood-ratio test, which is approximate due to finite-size effects. k: the penalty constant in AIC. traceThe R-sig-mixed modeling FAQ says the following regarding this: Tests of single parameters. From worst to best: Wald Z-tests; For balanced, nested LMMs where df can be computed: Wald t-tests; Likelihood ratio test, either by setting up the model so that the parameter can be isolated/dropped (via anova or drop1), or via computing likelihood profiles The Likelihood-Ratio Test (LRT) is a statistical test used to compare the goodness of fit of two models based on the ratio of their likelihoods. This article will use the LRT to compare two models which aim to predict a .
One-way ANOVA is generalized to all distributions. Here gamma random variables are created with different shapes. The one way test has a small p value and provides confidence intervals with 95% confidence for the whole set.Denominator degrees of freedom for an F test. If NULL these are estimated from the model. Use Inf for a chi-squared test. method: If "Wald", the Wald-type test; if "LRT" the Rao-Scott test based on the estimated log likelihood ratio; If "WorkingWald" the Wald-type test using the variance matrix under simple random sampling. lrt.approximation
Tour Start here for a quick overview of the site Help Center Detailed answers to any questions you might have Meta Discuss the workings and policies of this siteThis function runs the Wald and likelihood-ratio approaches for testing differential item functioning (DIF) with two or more groups. This is primarily a convenience wrapper to the multipleGroup function for performing standard DIF procedures. Independent models can be estimated in parallel by defining a parallel object with mirtCluster, which will help to decrease . In addition to @Henry's answer and to @PeterEllis' comment, here are a few comments about the R code itself: The third argument of mlog1 is sdev. You therefore need sdev in out1 and out2 (not sd); The likelihood ratio test is the logarithm of the ratio between two likelihoods (up to a multiplicative factor).
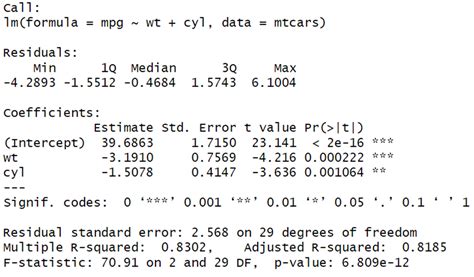
rdrr.io Find an R package R language docs Run R in your browser. . Digital Gene Expression Likelihood Ratio Test data and results - class . The null model is the model to which the full model is compared, and is fit using glmFit and dropping selected column(s) (i.e. coefficient(s)) .
As alternative to the formula one can give the indexes of the ordered effects to test (a vector of integers). To test only the intercept specify test = ~ - . or test = 1. values: Null hypothesis values, default values are 0. For testing the specific hypothesis B1=1, B4=2, B5=0 we specify test= ~B1+B4+B5-1 and values=c(1, 2,0). firth
The usual way to test if the interaction is significant is to do a likelihood ratio test (e.g. see discussion on R-Sig-ME). To do that you have to also estimate a model without interaction and you'll also have to use method="ML":The G-test uses the log of the ratio of two likelihoods as the test statistic, which is why it is also called a likelihood ratio test or log-likelihood ratio test. The formula to calculate a G-statistic is: G = 2 * sum(x * log(x / E)) where E are the expected values. Since this is chi-square distributed, the p value can be calculated in R with:The likelihood ratio test: which tests if the full model (the model with all the predictors included) fits the data better than the null model (the model with no variables). In our case, the LogLik.diff is -115.88 with p < 0.001, which means that adding the .
WEBDicionário online de Português. Antônimos de confiável: infiel, traiçoeiro, desleal, traidor, inconfiável, suspeito, inconsistente, dragão, baranga, canhão, ignorar, acesse e veja .
r package for dropping terms for likelihood ratio test|likelihood ratio test example